Machine control activity
1 Basic Control Flow
首先回答 Q1:为什么 JZ 和 JE 指令相同?
对于 JZ,即 jump if zero,在跳转之前,我们首先需要将其与 0 做差,判断结果的 ZF 是否等于 1。对于 JE,我们首先将两数做差(也可以使用testq指令?),然后判断 ZF 是否等于 1。JZ 和 JE 都是对 ZF 进行判断,然后进行跳转。
然后我们回答 Q2:首先阅读jumps.S。我们发现jumps.S就是以jump_insns开头的一群跳转指令的集合。然后我们输入如下指令:
$ as jumps.S -o jumps.o
$ objdump -d jumps.o其结果如下:
jumps.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <jump_insns>:
0: eb 34 jmp 36 <destination>
2: 70 32 jo 36 <destination>
4: 71 30 jno 36 <destination>
6: 72 2e jb 36 <destination>
8: 72 2c jb 36 <destination>
a: 72 2a jb 36 <destination>
c: 73 28 jae 36 <destination>
e: 73 26 jae 36 <destination>
10: 73 24 jae 36 <destination>
12: 74 22 je 36 <destination>
14: 74 20 je 36 <destination>
16: 75 1e jne 36 <destination>
18: 75 1c jne 36 <destination>
1a: 76 1a jbe 36 <destination>
1c: 76 18 jbe 36 <destination>
1e: 77 16 ja 36 <destination>
20: 77 14 ja 36 <destination>
22: 78 12 js 36 <destination>
24: 79 10 jns 36 <destination>
26: 7c 0e jl 36 <destination>
28: 7c 0c jl 36 <destination>
2a: 7d 0a jge 36 <destination>
2c: 7d 08 jge 36 <destination>
2e: 7e 06 jle 36 <destination>
30: 7e 04 jle 36 <destination>
32: 7f 02 jg 36 <destination>
34: 7f 00 jg 36 <destination>
0000000000000036 <destination>:
36: c3 retq这些指令的共同点就是都跳转到地址为 36 的destination处。此外,每个跳转指令的编码都是 2 个字节,第二个字节的值即为跳转的相对偏移地址,其值 = 目的地址 - 下一套指令的地址(因为执行到这里的时候 PC 已经指向下一条了),所以需要将该值增加到 PC 中,然后进行跳转。
接下来我们将.skip 97一行注释掉,然后再编译并且反汇编看看:
jumps.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <jump_insns>:
0: e9 bd 00 00 00 jmpq c2 <destination>
5: 0f 80 b7 00 00 00 jo c2 <destination>
b: 0f 81 b1 00 00 00 jno c2 <destination>
11: 0f 82 ab 00 00 00 jb c2 <destination>
17: 0f 82 a5 00 00 00 jb c2 <destination>
1d: 0f 82 9f 00 00 00 jb c2 <destination>
23: 0f 83 99 00 00 00 jae c2 <destination>
29: 0f 83 93 00 00 00 jae c2 <destination>
2f: 0f 83 8d 00 00 00 jae c2 <destination>
35: 0f 84 87 00 00 00 je c2 <destination>
3b: 0f 84 81 00 00 00 je c2 <destination>
41: 75 7f jne c2 <destination>
43: 75 7d jne c2 <destination>
45: 76 7b jbe c2 <destination>
47: 76 79 jbe c2 <destination>
49: 77 77 ja c2 <destination>
4b: 77 75 ja c2 <destination>
4d: 78 73 js c2 <destination>
4f: 79 71 jns c2 <destination>
51: 7c 6f jl c2 <destination>
53: 7c 6d jl c2 <destination>
55: 7d 6b jge c2 <destination>
57: 7d 69 jge c2 <destination>
59: 7e 67 jle c2 <destination>
5b: 7e 65 jle c2 <destination>
5d: 7f 63 jg c2 <destination>
5f: 7f 61 jg c2 <destination>
...
00000000000000c2 <destination>:
c2: c3 retqOracle 的 x86 Assembly Language Reference Manual中写道:
.skip integer, value
While generating values for any data section, the .skip directive causes integer bytes to be skipped over, or, optionally, filled with the specified value.
将 97 改为 98,再次处理后查看:
jumps.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <jump_insns>:
0: e9 c2 00 00 00 jmpq c7 <destination>
5: 0f 80 bc 00 00 00 jo c7 <destination>
b: 0f 81 b6 00 00 00 jno c7 <destination>
11: 0f 82 b0 00 00 00 jb c7 <destination>
17: 0f 82 aa 00 00 00 jb c7 <destination>
1d: 0f 82 a4 00 00 00 jb c7 <destination>
23: 0f 83 9e 00 00 00 jae c7 <destination>
29: 0f 83 98 00 00 00 jae c7 <destination>
2f: 0f 83 92 00 00 00 jae c7 <destination>
35: 0f 84 8c 00 00 00 je c7 <destination>
3b: 0f 84 86 00 00 00 je c7 <destination>
41: 0f 85 80 00 00 00 jne c7 <destination>
47: 75 7e jne c7 <destination>
49: 76 7c jbe c7 <destination>
4b: 76 7a jbe c7 <destination>
4d: 77 78 ja c7 <destination>
4f: 77 76 ja c7 <destination>
51: 78 74 js c7 <destination>
53: 79 72 jns c7 <destination>
55: 7c 70 jl c7 <destination>
57: 7c 6e jl c7 <destination>
59: 7d 6c jge c7 <destination>
5b: 7d 6a jge c7 <destination>
5d: 7e 68 jle c7 <destination>
5f: 7e 66 jle c7 <destination>
61: 7f 64 jg c7 <destination>
63: 7f 62 jg c7 <destination>
...
00000000000000c7 <destination>:
c7: c3 retq下一个问题是:为什么会这样?指令
eb f0又是做什么的?This happens for each instruction that needs to encode a change in %rip larger than 0x7F.(源自Solution)
2 Comparisons and Conditional Set Instructions
运行gdb ./cmp-set,输入r,提示如下:
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/gwen/Documents/report/code/15213/Ch3 Machine Level Programming/machine-control/cmp-set
This program should be run inside GDB:
$ gdb /home/gwen/Documents/report/code/15213/Ch3 Machine Level Programming/machine-control/cmp-set
(gdb) r
If you didn't run it that way, it will now crash.
Otherwise, you will get the (gdb) prompt back.
Type 'c' (short for 'continue') at the (gdb) prompt.
Program received signal SIGTRAP, Trace/breakpoint trap.
main (argc=<optimized out>, argv=<optimized out>) at machine-control/cmp-set.c:43
43 machine-control/cmp-set.c: No such file or directory.输入c,提示如下:
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Besides 'main', this program defines three functions:
'sete', 'seta', and 'setg'.
Use the 'disassemble' command on each to see their code.
Then, as instructed in the handout, use the 'call' command
to call them with various arguments.
When you have answered all the questions in this section of
the handout, use the 'c' command to go on.
Program received signal SIGTRAP, Trace/breakpoint trap.
main (argc=<optimized out>, argv=<optimized out>) at machine-control/cmp-set.c:45
45 in machine-control/cmp-set.c分别使用disassemble命令来查看sete,seta和setg三条指令,使用call命令来调用他们,完成任务后使用c来继续。
sete反汇编结果如下:
(gdb) disassemble sete
Dump of assembler code for function sete:
0x0000000000401178 <+0>: cmp %si,%di
0x000000000040117b <+3>: sete %al
0x000000000040117e <+6>: movzbl %al,%eax
0x0000000000401181 <+9>: retq
End of assembler dump.在sete中,%si和%di包含参数,%eax中包含返回值。该函数的 C 代码还原如下:
这里到底是
uint16_t还是int16_t?有区别吗?
#include <stdint.h>
sete(uint16_t si, uint16_t di)
{
return si == di;
}seta函数的反汇编结果如下:
(gdb) disassemble seta
Dump of assembler code for function seta:
0x000000000040118c <+0>: cmp %si,%di
0x000000000040118f <+3>: seta %al
0x0000000000401192 <+6>: movzbl %al,%eax
0x0000000000401195 <+9>: retq
End of assembler dump.seta比较的是无符号数,其 C 语言代码如下:
#include <stdint.h>
sete(uint16_t si, uint16_t di)
{
return di > si;
}setg函数的反汇编结果如下:
(gdb) disassemble setg
Dump of assembler code for function setg:
0x0000000000401182 <+0>: cmp %si,%di
0x0000000000401185 <+3>: setg %al
0x0000000000401188 <+6>: movzbl %al,%eax
0x000000000040118b <+9>: retq
End of assembler dump.setg比较的是有符号数,其 C 语言代码如下:
#include <stdint.h>
sete(int16_t si, int16_t di)
{
return di > si;
}注意setg和seta有区别。
对不同组别的值分别调用sete,seta和setg,其值如下:
| arg1 | arg2 | sete | setg | seta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | - | - |
| 0 | 1 | - | - | - |
| 1 | 0 | - | 1 | 1 |
| -1 | 0 | - | - | 1 |
| 0 | -1 | - | 1 | - |
| 32768 | 32767 | - | - | 1 |
| 32767 | 32768 | - | 1 | - |
| 32768 | 32768 | 1 | - | - |
| 32768 | −32768 | 1 | - | - |
| −32768 | 32768 | 1 | - | - |
| −32768 | −32768 | 1 | - | - |
从-1和0的两行比较可以看得出来,seta是先将负数转化为unsigned类型的数,然后再相减。当数字的值超过signed类型范围后,会转化为负数,然后再比较。此处32768在进行有符号数比较时都被转化为-32768了
3 Tests and Conditional Move Instructions
输入下列指令开启当前 Activity:
$ gdb ./test-cmov
(gdb) r得到如下提示:
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/gwen/Documents/report/code/15213/Ch3 Machine Level Programming/machine-control/test-cmov
This program should be run inside GDB:
$ gdb /home/gwen/Documents/report/code/15213/Ch3 Machine Level Programming/machine-control/test-cmov
(gdb) r
If you didn't run it that way, it will now crash.
Otherwise, you will get the (gdb) prompt back.
Type 'c' (short for 'continue') at the (gdb) prompt.
Program received signal SIGTRAP, Trace/breakpoint trap.
main (argc=<optimized out>, argv=<optimized out>) at machine-control/test-cmov.c:43
43 machine-control/test-cmov.c: No such file or directory.
(gdb)输入c继续,得到如下提示:
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Besides 'main', this program defines three functions:
'cmove', 'cmovs', and 'cmovc'.
Use the 'disassemble' command on each to see their code.
Then, as instructed in the handout, use the 'call' command
to call them with various arguments.
When you have answered all the questions in this section of
the handout, use the 'c' command to go on.
Program received signal SIGTRAP, Trace/breakpoint trap.
main (argc=<optimized out>, argv=<optimized out>) at machine-control/test-cmov.c:45
45 in machine-control/test-cmov.c对cmove,cmovs和cmovc三个函数分别进行反汇编可以得到如下结果:
(gdb) disassemble cmove
Dump of assembler code for function cmove:
0x00000000004005b3 <+0>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004005b8 <+5>: test %di,%di
0x00000000004005bb <+8>: cmove %esi,%eax
0x00000000004005be <+11>: retq
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) disassemble cmovs
Dump of assembler code for function cmovs:
0x00000000004005bf <+0>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004005c4 <+5>: test %di,%di
0x00000000004005c7 <+8>: cmovs %esi,%eax
0x00000000004005ca <+11>: retq
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) disassemble cmovc
Dump of assembler code for function cmovc:
0x00000000004005cb <+0>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004005d0 <+5>: test %di,%di
0x00000000004005d3 <+8>: cmovb %esi,%eax
0x00000000004005d6 <+11>: retq
End of assembler dump.首先我们需要了解cmov三条指令分别是做什么的,可以参见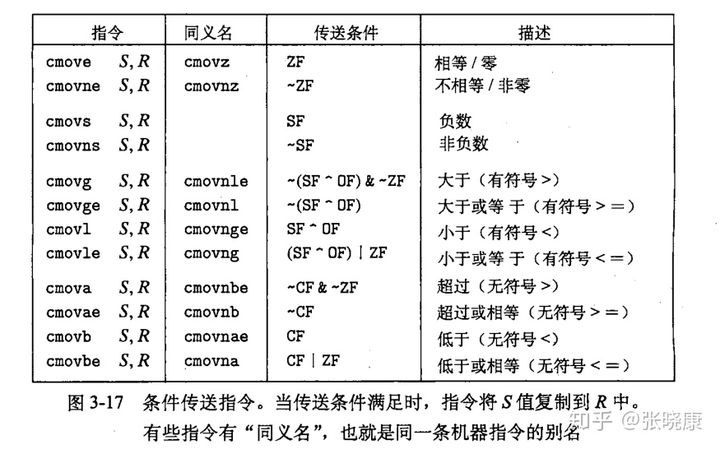
其中cmove是当ZF = 1时为 1(相等或等于 0),cmovs是当SF = 1时为 1(为负数),cmovb时当CF = 1时为 1(低于,无符号<)。上述三个函数的两个传入参数是%di和%esi。若%di满足条件,则将返回值设置为%esi。否则%eax = 0。由此可得,arg1是%di,arg2是%esi。
Q1: 为什么cmovc中使用的是cmovb指令?因为cmovc指令的意义是move if carry
Q2: test指令使用的什么寄存器?使用的是%di,2 个字节。
接下来填表:
Arg 1(%di) | Arg 2(%esi) | cmove(相等/0) | cmovs(负数) | cmovb(无符号<) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | |||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | |||
| 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 2 | |||
| −1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| −1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| −1 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 32767 | 1 | |||
| 32768 | 1 | 1 |
未填写部分全为 0。从上表我们可以看到cmove只有在%di等于 0 时,才会等于%esi。而%esi只有在为%di负数时,才会等于%esi(此外,如果%di的值超过了有符号数的上界,如32768,那么其会被转化为-32768,也就是最后一行,那么%di也是负数,因此%eax被赋值为 1)。此外,cmovb一直等于 0,因为这里没有无符号的小于。
4 Loops
按照 handout 提示输入objdump -d loops.o,得到如下结果:
loops.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <forLoop>:
0: ba 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edx
5: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
a: 39 f0 cmp %esi,%eax
c: 7d 0b jge 19 <forLoop+0x19>
e: 48 63 c8 movslq %eax,%rcx
11: 03 14 8f add (%rdi,%rcx,4),%edx
14: 83 c0 01 add $0x1,%eax
17: eb f1 jmp a <forLoop+0xa>
19: 89 d0 mov %edx,%eax
1b: c3 retq该汇编代码的 C 语言形式如下:
int forLoop(int* x, int len) {
int ret = 0;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ret += x[i];
}
return ret;
}000000000000001c <whileLoop>:
1c: ba 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edx
21: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
26: 39 f0 cmp %esi,%eax
28: 7d 0b jge 35 <whileLoop+0x19>
2a: 48 63 c8 movslq %eax,%rcx
2d: 03 14 8f add (%rdi,%rcx,4),%edx
30: 83 c0 01 add $0x1,%eax
33: eb f1 jmp 26 <whileLoop+0xa>
35: 89 d0 mov %edx,%eax
37: c3 retq该循环的 C 形式代码如下:
int whileLoop (int* x, int len) {
int ret = 0;
while (i < len) {
ret += x[i];
i++;
}
return ret;
}0000000000000038 <doWhileLoop>:
38: ba 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edx
3d: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
42: 48 63 c8 movslq %eax,%rcx
45: 03 14 8f add (%rdi,%rcx,4),%edx
48: 83 c0 01 add $0x1,%eax
4b: 39 f0 cmp %esi,%eax
4d: 7c f3 jl 42 <doWhileLoop+0xa>
4f: 89 d0 mov %edx,%eax
51: c3 retqdoWhileLoop的 C 循环代码如下:
int doWhileLoop (int* x, int len) {
int ret = 0;
int i = 0;
do {
ret += x[i];
i++;
} while (i < len);
return ret;
}5 Switch Statements
switch语句汇编代码如下:
switcher:
cmpq $7 , %rdi
ja .L2
jmp *.L4(, %rdi , 8)
.L7:
xorq $15 , %rsi
movq %rsi , %rdx
.L3:
leaq 112(% rdx), %rdi
jmp .L6
.L5:
leaq (%rdx , %rsi), %rdi
salq $2 , %rdi
jmp .L6
.L2:
movq %rsi , %rdi
.L6:
movq %rdi , (% rcx)
ret
.section .rodata
.L4:
.quad .L3 ;;x = 0 -> rdi = rdx + 112; break;
.quad .L2 ;;x = 1 -> default
.quad .L5 ;;x = 2 -> rdi = rdx + rsi; rdi = rdi << 2; break;
.quad .L2 ;;x = 3 -> default
.quad .L6 ;;x = 4 -> *rcx = rdi; break;
.quad .L7 ;;x = 5 -> rsi = rsi ^ 15; rdx = rsi;
.quad .L2 ;;x = 6 -> default
.quad .L5 ;;x = 7 -> rdi = rdx + rsi; rdi = rdi << 2; break;其还原的 C 语句代码如下:
// 1, 3, 6没有;只有 0,2,4,5,7
// %rdi = a and val , %rsi = b, %rdx = c, %rcx = dest
void switcher(long a, long b, long c, long *dest) {
long val;
switch (a) {
case 5:
c = b ^ 15;
case 0:
val = c + 112;
break;
case 2:
case 7:
val = (c + b) << 2;
break;
case 4:
val = a;
break;
default:
val = b;
}
*dest = val;
}注意case 4中,按理来说.L4时val = a而不是*dest = val(汇编来看)。这里我们再将 C 编译成汇编语句时,对 C 语言的语句做了一个优化,将*dest = val转化为两句:
val = a;
*dest = val;这样转化的原因是在 C 语言中*dest = val是所有语句共同需要执行的部分,因此我们将它放在switch语句之外,而将val = a放在语句内。这样语句前后意思是一样的,而switch语句的目的也达到了。而汇编层面做了优化,将*dest = val直接放在.L6处,其他语句执行完后跳转到.L6。